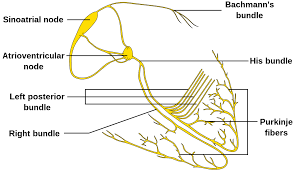
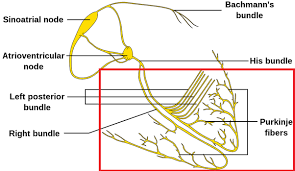
 The His- Purkinje fiber tissue or subendocardial branches are located in the inner ventricular walls of the heart, just beneath the endocardium in the subendocardium.
The His- Purkinje fiber tissue or subendocardial branches are located in the inner ventricular walls of the heart, just beneath the endocardium in the subendocardium.
The His-Purkinje fibers are specialised conducting fibers composed of electrically excitable cells that are larger than cardiomyocytes.
This system has fewer myofibrils and many mitochondria which cardiac action potentials more quickly and efficiently than any other cells in the heart.
The His-Purkinje fibers allow the heart’s conduction system to create synchronized contractions of its ventricles.
It is essential for maintaining a consistent heart rhythm.
Purkinje fibers are found just beneath the endocardium.
The electrical origin of atrial Purkinje fibers comes from the sinoatrial node.
The Purkinje fibers rapidly conduct impulses.
The Purkinje fibers have numerous fast voltage-gated sodium channels and mitochondria, and fewer myofibrils than the surrounding muscle tissue.
Heart rate is governed by autonomic nervous system influences.
The Purkinje fibers are influenced by electrical discharge from the sinoatrial node.
The Purkinje fibers during ventricular contraction carry the impulse from both the left and right bundle branch to the myocardium of the ventricles. Thanks
These impulses cause the muscle tissue of the ventricles to contract and generate force to eject blood out of the heart ventricles either to the pulmonary circulation from the right ventricle or to the systemic circulation from the left ventricle.
If peacemaking ability is impaired the Purkinje fibers have the ability of firing at a rate of 15-40 beats per minute.
Normally the SA node can fire at 60-100 beats per minute.
Purkinje fibers generate action potentials at a slower rate than sinoatrial node, serving as the last resort when other pacemakers fail.
Purkinje fibers generate action potential
capability is normally suppressed.
When a Purkinje fiber fires , it is referred to as a premature ventricular contraction or PVC, or in other situations can be a ventricular escape.
The Bundle of His is a collection of heart muscle cells specialized for electrical conduction.
It transmits the electrical impulses from the AV node which is located between the atria and the ventricles to the point of the apex of the fascicular branches via the bundle branches.
The fascicular branches then lead to the Purkinje fibers, which provide electrical conduction to the ventricles, causing the cardiac muscle of the ventricles to contract at a paced interval.
The bundle, originates near the orifice of the coronary sinus, undergoes slight enlargement to form the AV node.
The bundle of His, passes into the ventricular septum and divides into two bundle branches, the left and right bundles.
Sometimes the left and right bundles of His are called Purkinje fibers.
The bundle of His transmits impulses from the atrioventricular node, located at the anterior-inferior end of the interatrial septum, to the ventricles of the heart.
The bundle of His branches into the left and the right bundle branches, which run along the interventricular septum.
The left bundle branch further divides into the left anterior and the left posterior fascicles, which give rise to thin filaments known as Purkinje fibers.
The ventricular conduction system comprises the bundle branches and the Purkinje networks.
It takes about 0.03–0.04 seconds for the impulse to travel from the bundle of His to the ventricular muscle.
Disorders affecting the electrical conduction system of the heart are called heart blocks.
Heart blocks are divided into different categories based on the location of the impairment.
Damage to any of the conducting cells in or below the bundle of His are collectively ref2242ed to as infra-Hisian blocks.
Blocks that occur in the right or left bundle branches are called bundle branch blocks.
Blocks that occur in either the left anterior or the left posterior fascicles are called fascicular blocks, or hemiblocks.
When both the right bundle branch and either the left anterior fascicle or the left posterior fascicle are blocked are collectively ref2242ed to as bifascicular blocks.
When the right bundle branch, the left anterior fascicle, and the left posterior fascicle are blocked is called trifascicular block.
Infra-hisian blocks limit the heart’s ability to coordinate the activities of the atria and ventricles, which usually results in a decrease in its efficiency in pumping blood.
Normally initiates electrical depolarization throughout the cardiac ventricles.
The electrical conduction through the His-Purkinje system and bundle branches is approximately 10 times the myocyte-myosite conduction velocity.
