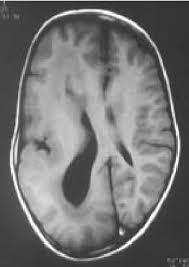
 Hemimegalencephaly (HME), or unilateral megalencephaly.
Hemimegalencephaly (HME), or unilateral megalencephaly.
HME is a rare congenital disorder affecting all or a part of a cerebral hemisphere.
It causes severe seizures, which are often frequent and hard to control.
Most patients will need removal or disconnection of the affected hemisphere as the best chance to control seizures.
Uncontrolled seizures often cause progressive intellectual disability and brain damage and stop development.
Seizures are the main symptom of HME, and usually begin soon after birth: but sometimes commence during later infancy or, rarely, during early childhood.
There can be as many as hundreds of seizures daily.
Other findings:
Asymmetrical or enlarged head
Developmental delay
Progressive weakness of half the body
Progressive blindness of half the body
Genetics-PIK3CA mutations with somatic activation of AKT3 causes hemispheric developmental brain malformations.
It has an excessive neuronal proliferation and hamartomatous overgrowth affecting the cortical formation.
Diagnosis:
It should be suspected in infants or children with intractable, frequent seizures.
CT brain scan shows affected part is distorted and enlarged.
Ultrasound can display asymmetrical brain hemispheres.
The process can be diagnosed prenatally, but many cases are undiagnosed until seizures occur.
TREATMENT:
The primary treatment is removing or disconnecting the affected cerebral hemisphere.
Such surgery is associated with a high mortality.
Reports of a vegetative state and seizures recurrent seizures in the healthy hemisphere.
Surgery should be done as early as possible to minimize damage caused by seizures, and the remaining brain will be more successful at its expanded role.Thanks
