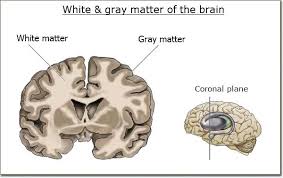
 Refers to the cortex of the brain, which contains nerve cell bodies.
Refers to the cortex of the brain, which contains nerve cell bodies.
Appears darker than the white matter, the part of the brain that contains myelinated nerve fibers.
A major component of the central nervous system, consisting of neuronal cell bodies, dendrites and unmyelinated axons, glial cells and capillaries.
Made up of neuronal cell bodies.
- The volume of the gray matter, which represents the total number of brain cells, reaches its peak during childhood, at about the age of 7.
Includes regions of the brain involved in muscle control, sensory perception such as seeing and hearing, memory, emotions, and speech.
The gray matter refers to surface neural matter of the cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum, thalamus, hypothalamus, basal ganglia – putamen, globus pallidus, nucleus accumbens; septal nuclei, deep cerebellar nuclei, and spinal gray matter of the anterior horn, lateral horn, posterior horn.
Correlations have been found between gray matter volume and measures of semantic and short-term memory.
Structural differences in gray matter may be associated with psychiatric disorders.
Smoking associated with loss of gray matter.
