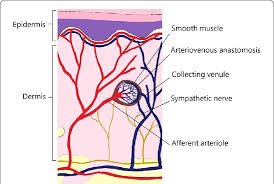
 A glomus body, or glomus organ, is a component of the dermis layer of the skin, involved in body temperature regulation.
A glomus body, or glomus organ, is a component of the dermis layer of the skin, involved in body temperature regulation.
The glomus body is a small arteriovenous anastomosis surrounded by a capsule of connective tissue.
Glomera are most numerous in the fingers and toes.
The role of the glomus body is to shunt blood away from the skin surface when exposed to cold temperatures.
It prevents heat loss, and allowing maximum blood flow to the skin in warm weather to allow heat to dissipate.
The glomus body has high sympathetic tone and can lead to near complete vasoconstriction.
Endothelial cells form a single, continuous layer that lines all vascular segments.
The arteriovenous shunt of the glomus body is a normal anatomic shunt as opposed to an abnormal arteriovenous fistula.
