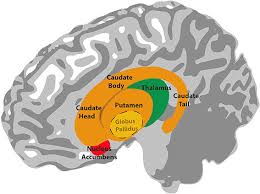
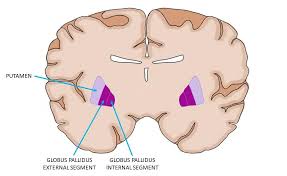
The globus pallidus (GP), is a subcortical structure of the brain.
It consists of two adjacent segments, one external, and one internal.
It is part of the telencephalon, but retains close functional ties with the subthalamus in the diencephalon – both of which are part of the extrapyramidal motor system.
The globus pallidus is a major component of the basal ganglia, with principal inputs from the striatum, and principal direct outputs to the thalamus and the substantia nigra.
Almost all pallidal neurons are very large, parvalbumin-positive, with very large dendritic arborizations.
The globus pallidus is traversed by the numerous myelinated axons of the striato-pallidonigral bundle that give it the pale appearance from which it is named.
The globus pallidus is divided into two parts by the medial medullary lamina.
These are the internal globus pallidus (GPi) and the external globus pallidus (GPe).
Both parts are composed of closed nuclei surrounded by myelinic walls.
The globus pallidus is a part of the basal ganglia, a group of structures located in the brain that are involved in movement control, memory, and emotions.
The internal segment of the globus pallidus receives input from other structures in the basal ganglia and sends output to the thalamus, which in turn sends information to various parts of the brain.
The internal globus pallidus is regarded as an output structure of the basal ganglia.
It processes input from nucleus accumbens and the striatum, and sends input to the cerebral cortex via the thalamus.
It is critical for the functioning of the basal ganglia.
The internal segment also plays a role in inhibiting unwanted movements and is involved in regulating muscle tone.
The external segment of the globus pallidus is thought to regulate the activity of the internal segment by inhibiting its output.
It also receives input from other parts of the basal ganglia and sends output to the subthalamic nucleus, another structure involved in movement control.
The globus pallidus, along with other structures in the basal ganglia, helps to coordinate and control voluntary movements by influencing the activity of lower motor neurons in the brainstem and spinal cord.
Dysfunction of the globus pallidus and other parts of the basal ganglia can lead to movement disorders such as Parkinson’s disease and Huntington’s disease.
The ventral pallidum lies within the substantia innominata and receives efferent connections from the ventral striatum, the nucleus accumbens and the olfactory tubercle.
Its function is to serve as a limbic-somatic motor interface, and it is involved in the planning and inhibition of movements from the dorsal striatopallidal complex.
The globus pallidus is a structure in the brain involved in the regulation of voluntary movement.
It is part of the basal ganglia, which, among many other functions, regulate movements that occur on the subconscious level.
If the globus pallidus is damaged, it can cause movement disorders, as its regulatory function will be impaired.
A pallidotomy, is a procedure in which a lesion is created to reduce involuntary muscle tremors.
The globus pallidus has a primarily inhibitory action that balances the excitatory action of the cerebellum when it comes to movement.
These two systems work in harmony with each other to allow smooth and controlled movements.
Imbalances can result in tremors, jerks, and other movement problems, as seen in some people with progressive neurological disorders characterized by symptoms like tremors.
The basal ganglia acts on a subconscious level, requiring no conscious effort to function.
The globus pallidus is involved in the constant subtle regulation of movement that allows people to participate in a wide variety of activities with a minimal level of disruption.
The two pallidal nuclei and the two parts of the substantia nigra the pars compacta and pars reticulata, constitute a high-frequency autonomous pacemaker.
