 A system based on evaluation of nuclear grade and glandular differentiation of Prostate cancer.
A system based on evaluation of nuclear grade and glandular differentiation of Prostate cancer.
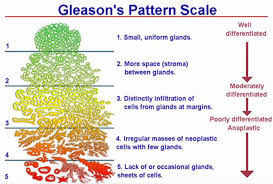
Gleason grades are based on prostate cancer morphology to describe the loss of tissue structure and order and are strongly correlated with the aggressiveness of the disease and patient outcome.
Gleason scoring categories arrange tumor tissue into patterns from 1, low risk, to 5 high risk.
Assigns grades to the primary and secondary patterns and combined this grade into the score (scored as 2-10).
Recognizes 5 different patterns (grades) of PCa cells as seen under a microscope.
Gleason score is always shown as the sum of 2 numbers (e.g., 3+4=7) based on the 2 highest proportions of the most aggressive pattern in each biopsy needle sample.
GG1 – low risk (Gleason score 3+3=6)
GG2-favorable intermediate risk (Gleason score 3+4=7)
GG3- unfavorable intermediate risk (Gleason score 4+3=7)
GG4 – high risk (Gleason score 4+4=8)
GG5 – high risk (Gleason score 9 or 10)
Has prognostic value in preprostatectomy and preradiotherapy needle biopsy specimens.
The most widely accepted system for pathological grading of prostate adenocarcinomas.
Consistent reproducibility to independently predict disease outcomes.
Is associated with substantial interobserver disagreements.
Assigns a grade to the tumor based on tumor architecture viewed under relatively low power microscopy.
The more the glandular architecture deviates from normal the higher the Gleason score.
Accounts for the fact that prostate cancer is often multifocal and there are different Gleason patterns even within a single lesion.
The Gleason score is underestimated from prostate biopsy on 50% of cases compared to pathological specimen.
At 15.5 years of follow-up an estimated 4-5 year loss of life expectancy in men treated with watchful waiting for Gleason 5 to 7 prostate cancer.
Most small Gleason pattern 3 or less lesions could be considered nonmalignant.
Translocation of TMPRSS2-ERG, PTEN deletion, sustained vascular endothelial growth-factor induced angiogenesis, and resistance to apoptosis from DAD1 expression are most common in Gleason pattern 4 lesions, and are absent or at low levels in Gleason pattern 3 lesions.
Molecular and histologic patterns of Gleason 3 lesions remain stable or even involute.
Gleason pattern 4 lesions have most of the molecular characteristics of cancer.
Gleason 6 or less low-grade prostate cancer.
Surgical series report a rate of metastases of near zero in surgically confirmed Gleason 6 prostate cancer.
The 15 year prostate specific mortality rate for pathologic Gleason 6 is only 0.2% (Eggener SE).
Most Gleason 6 cancers have innocent genetic features and no risk of metastases-they have little indication for treatment in most patients.
Gleason 6 disease can demonstrate the ability to invade pathologically, it does not appear to have the propensity to invade clinically.
In patients with high risk Gleason score of eight or greater at biopsy, there is suboptimal PSA control at five years following prostatectomy, and in the setting of uninvolved seminal vesicles or lymph nodes, the dominant pattern of failure is local, and therefore postoperative radiotherapy should be considered.
