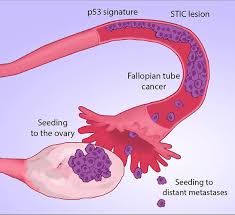
 Primary fallopian tube cancer (PFTC), is a malignant neoplasm that originates from the fallopian tube.
Primary fallopian tube cancer (PFTC), is a malignant neoplasm that originates from the fallopian tube.
Tubal cancer is thought to be a relatively rare primary cancer among women, accounting for 1 to 2 percent of all gynecologic cancers.
In the US, tubal cancer had an incidence of 0.41 per 100,000 women:, recent evidence suggests tubal cancer to be much more frequent.
Incidence 3.6 per million.
The location of the fallopian tubes makes it difficult to reach an early diagnosis of FTC.
Symptoms are nonspecific, and may consist of pain and vaginal discharge or bleeding.
A pelvic mass may be detected on a routine gynecologic examination.
The most common cancer type within this disease is adenocarcinoma.
Rarer forms of tubal neoplasm include leiomyosarcoma, and transitional cell carcinoma.
Secondary tubal cancer usually originates from cancer of the ovaries, the endometrium, the GI tract, the peritoneum, and the breast.
A pelvic examination may detect an adnexal mass.
A CA-125 blood test is a nonspecific test that tends to be elevated in patients with tubal cancer.
Other tests are a gynecologic ultrasound examination, a CT scan, or an MRI of the pelvis.
Staging
Stage 0 :Carcinoma in situ
Stage I :Growth limited to fallopian tubes
Stage II :Growth involving one or both fallopian tubes with extension to pelvis
Stage III:Tumor involving one or both fallopian tubes with spread outside pelvis
Stage IV :Growth involving one or more fallopian tubes with distant metastases
Treatment
The initial approach to tubal cancer is generally surgical.
A total abdominal hysterectomy is an essential approach, removing the ovaries, the tubes, and the uterus with the cervix.
Peritoneal washings are taken, the omentum is removed, and pelvic and paraaortic lymph nodes are sampled.
In advanced cases when the cancer has spread to other organs and cannot be completely removed, cytoreductive surgery is used to lessen the tumor burden for subsequent treatments.
Surgical treatments are typically followed by adjuvant, usually platinum-based, chemotherapy.
Radiation therapy is used for palliative or curative indications.
Prognosis depends to a large degree on the stage of the condition.
About half of the patients with advanced stage disease survived 5 years with a surgical approach followed by cisplatinum-based chemotherapy.
Demographic distribution is similar to that of ovarian cancer.
The highest incidence is found in White, women aged 60–79.
Women with mutations of BRCA1 and BRCA2 are at higher risk for the development of PFTC.
The fallopian tube has an outer muscular layer and an inner mucosal layer with ciliated columnar cells, secretary cells, and intercalated cells.
The fimbriated end of the fallopian tube has been implicated in many adenocarcinomas thought previously to have a arisen in the ovary.
The prophylactic removal of apparently normal tubes and ovaries from women would BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations show that the fimbriated end of the fallopian tube harbors serous carcinoma in 2 to 7% of specimens.
