 Eye crystals refer to crystalline deposits that can occur in various parts of the eye.
Eye crystals refer to crystalline deposits that can occur in various parts of the eye.
These deposits can be composed of various substances: lipids, proteins, or minerals.
These deposits can be associated with specific diseases or systemic conditions.
Bietti crystalline dystrophy, is a genetic disorder characterized by the accumulation of small, yellow or white crystal-like deposits in the retina, leading to progressive vision loss.
Bietti crystalline dystrophy condition is associated with mutations in the CYP4V2 gene and typically presents with symptoms such as night blindness and peripheral vision loss.
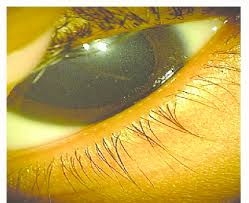
Crystalline keratopathy, which can occur in patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), where immunoglobulin crystals accumulate in the cornea, leading to visual impairment
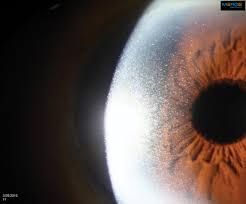
Ocular cystinosis is another condition where cystine crystals accumulate in the cornea and conjunctiva, causing photophobia and other visual disturbances, and is a manifestation of the systemic disorder cystinosis, which involves the accumulation of cystine within lysosomes.
Subconjunctival urate crystals can occur in patients with gout, where urate crystals deposit in the subconjunctival space, often detected incidentally during eye examinations.
