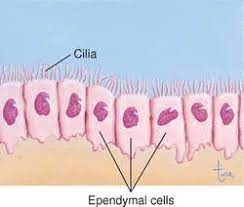
 Ependymal cells are specialized glial cells that line the ventricles and central canal of the spinal cord in the central nervous system (CNS).
Ependymal cells are specialized glial cells that line the ventricles and central canal of the spinal cord in the central nervous system (CNS).
These cells form a barrier between the brain and the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), which circulates in the ventricles and around the brain and spinal cord.
Ependymal cells have a ciliated surface that facilitates the movement of CSF through the ventricles and the central canal of the spinal cord.
They also have stem cell-like properties and can differentiate into other cell types in response to injury or disease in the CNS.
Ependymoma is a type of brain tumor that arises from the ependymal cells.
These tumors are typically slow-growing and can occur in both adults and children.
Ependymomas can cause symptoms such as headaches, nausea, and vomiting, and treatment typically involves surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy.
