 Marker for increased melanoma risk with and 8-fold greater association with malignant melanoma.
Marker for increased melanoma risk with and 8-fold greater association with malignant melanoma.
One atypical nevi associated with a 2-fold risk of malignant melanoma while 10 or more confer a 12-fold increased risk.
Often associated with familial melanomas, but are seen in 30-50% of sporadic cases.
Individuals with dysplastic nevi have a 7% lifetime risk for melanoma.
Acquired pigmented lesions that develop during puberty and continue to develop and change throughout life.
Primarily develop on the trunk.
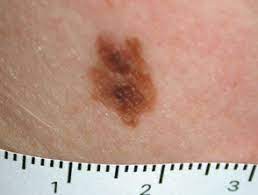
Share many features of malignant melanoma, including asymmetry, irregular border, color variation and diameter greater than 6 mm.
May occur up to hundreds of lesions.
Flat macules or slightly raised plaques, or target like lesions with darker center and irregular flat periphery.
Borders are usually irregular with variable pigmentation.
Tendency to occur on non-sun exposed as well as on sun exposed body surfaces.
Documented in family members and association with malignant melanoma referred to the heritable melanoma syndrome.
Heritable melanoma syndrome inherited as an autosomal dominant.
Consist of compound nevi with architectural and cytologic evidence of abnormal cell growth.
Single nevus cells start to replace normal basal cell layer along the dermoepidermal junction, producing lentiginous hyperplasia.
