 2164
2164
1066
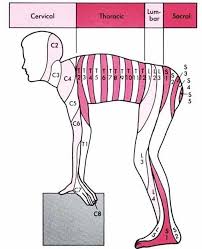
Each of the spinal nerves exits the spinal canal between two vertebrae.
The area of skin served by each of these nerves is called its dermatome.
The nerves from the upper cervical spine serve the skin of the neck.
The nerves from C5 to T1 go to the arms.
The nerves from T2 to L2 go to the chest and abdomen.
Nerves from L3 to S1 go to the skin of the legs.
Sacral nerves, and the coccygeal nerves, go to the groin.
When the C6 nerve is pinched, there is pain and numbness in the thumb and index finger.
When the L5 nerve is pinched, there is pain and numbness in the great toe..
List of Dermatomes of Commonly Injured Nerve Roots:
C5 – The area over the shoulder.
C5: The deltoid (the shoulder muscle that lifts the arm from the body) is innervated by nerves coming from C5.
In addition to shoulder weakness, this radiculopathy may lead to numbness in the shoulder and upper arm.
C6 – The thumb and part of the forearm.
C6: A C6 radiculopathy can lead to weakness in the biceps and wrist extensors.
In addition, there may be sensory abnormalities in the index and middle fingers, as well as part of the forearm.
C7 – The middle finger.
C7: Almost half (46 percent) of all cervical radiculopathies involve this nerve root.
The main weakness is in the triceps muscle that straightens the arm.
There may also be some sensory loss in part of the hand, such as the ring finger.
C8 – The smallest fingers and part of the forearm.
The nerves that exit the neural foramina in the lumbar spine go on to form the lumbar plexus, a complex anastamosis of different nerves.
These nerves go on to innervate the skin and muscles of the leg.
L4: The iliopsoas, which flexes the hip, may be weak, as may the quadriceps that extend the leg at the knee.
The knee and part of the lower leg may also be numbed.
L5: The ability to raise the point of the foot off the floor may be diminished, and the top surface of the foot may be numb.
This nerve root is involved in about 40 to 45 percent of lumbosacral radiculopathies.
S1: The ability to point the foot towards the floor (as if you were going to stand on tiptoe) is weakened, and there may be numbness of the small toe and sole of the foot.
This nerve root is involved in about 45 to 50 percent of lumbosacral radiculopathies.
L2-mid anterior thigh
L3-medial aspect of the knee
L4 – The thigh.
L4-The medial aspect of the ankle.
L5 – The medial part of the calf and foot, the big toe.
L5-The dorsum of the foot
S1 – The lateral part of the calf and foot, the smaller toes.
S2-S5- nerve roots supply the perianal and perineal region.
S1-S3 Sacral nerve roots evaluate the bulbocavernous reflex which can be demonstrated by applying pressure to the glans penis or clitoris while performing a rectal examination, the sphincter should contract.
