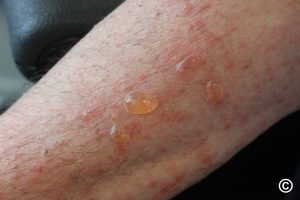
 A chronic, autoimmune, subepidermal disease that manifests with tense blisters.
A chronic, autoimmune, subepidermal disease that manifests with tense blisters.
It usually starts on the arms and legs and almost never involves the mucous membranes.
Bullous pemphigoid primarily affects elderly persons in the fifth through seventh decades of life; the average age at onset is 65 years.
Can last for weeks, months, or years.
The disease is marked by spontaneous remissions and exacerbations.
Rarely fatal.
Most patients experience remission in 1 to 5 years.
The various forms of bullous pemphigoid include:
Generalized bullous
Vesicular
Vegetative.
Generalized erythroderma.
Urticarial.
Nodular.
Acral
The diagnosis is established with a biopsy and examined with direct immunofluorescence.
Moderate-strength topical corticosteroids are the first line of treatment for Grover disease.
The most commonly used medications are anti-inflammatory agents such as corticosteroids, tetracyclines, and dapsone, and immunosuppressants such as azathioprine, methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil, and cyclophosphamide.
An oral corticosteroid may be needed to control bullous pemphigoid.
