 The most common lower respiratory tract infection in children.
The most common lower respiratory tract infection in children.
The leading cause for hospitalization for children.
Accounts for 100,000 hospital admissions annually.
Hospitalization rates are increasing.
Approximately 130,000 infants aemitted each year to hospitals with this disease.
Occasionally requires ventilators support and is rarely fatal.
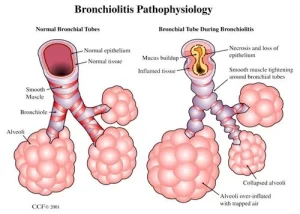
Usually of viral origin, with respiratory syncytial virus the most common cause.
Manifested by nasal flaring, dyspnea, chest retractions, tachypnea, wheezing, and crepitations.
Treatment is controversial, associated bronchodilators used commonly but have not been shown to be consistently beneficial.
Corticosteroids used in about 25% of hospitalized infants but their efficacy not consistently been demonstrated.
Schuh et al. in 2002 reported reductions in respiratory scores after 4 hours of oral dexamethasone compared to a control group treated with placebo, also the hospital admission rate was 19% for the steroid group vs 44% for those treated with placebo.
In a randomized, double blind study of 600 infants with moderate to severe disease there was no significant reduction in hospital admissions or improvement in respiratory status after 4 hours of observation following a single oral dose of 1 mg of dexamethasone per kg compared to infants given placebo (Corneli).
Adrenaline reduces mucosal swelling and is frequently used in an inhaled fashion resulting improve symptoms and reduces the need for hospitalizations in outpatients.
Inhaled adrenaline has not reduced the length of hospital stay in in patients with acute bronchiolitis.
