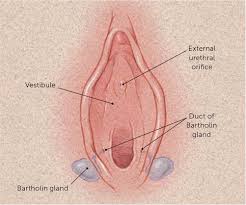
 The Bartholin’s glands are two pea-sized compound alveolar glands,located slightly posterior and to the left and right of the opening of the vagina.
The Bartholin’s glands are two pea-sized compound alveolar glands,located slightly posterior and to the left and right of the opening of the vagina.
They secrete mucus to lubricate the vagina.
BGs are homologous to bulbourethral glands in males.
Bartholin’s glands are located in the superficial perineal pouch in females.
The ducts are paired and they open on the surface of the vulva.[3]
Its nerve innervation and blood supply are via the pudendal nerve and external pudendal artery, respectively.
The superficial inguinal lymph nodes and pelvic nodes provide lymphatic drainage.
These glands are pea-sized (0.5–1.0 cm) and are lined with columnar epithelium.
The duct length is 1.5–2 cm and is lined with squamous epithelium.
These are located just beneath the fascia and their ducts drain into the vestibular mucosa, and secrete mucoid alkaline material.
The efferent ducts are composed of transitional epithelium, which merges into squamous epithelium as it enters the distal vagina.
The intimate relation between the enormously vascular tissue of the vestibular bulb and the Bartholin’s glands is responsible for the risk of hemorrhage associated with the removal of this latter structure.
The openings of the Bartholin’s glands are located on the posterior margin of the introitus bilaterally.
Bartholin’s glands secrete mucus to provide vaginal lubrication during sexual arousal, which may slightly moisten the labial opening of the vagina, serving to make contact with this sensitive area more comfortable.
Lbrication fluid is amount of about 6 grams per day, and contains high potassium and low sodium concentrations relative to blood plasma, with a slightly acidic pH of 4.7.
Bartholin’s glands may become blocked and inflamed resulting in pain.
A Bartholin’s cyst in turn can become infected and form an abscess.
Adenocarcinoma of the gland is rare and benign tumors and hyperplasia are even more rare.
Bartholin gland carcinoma is a rare malignancy that occurs in 1% of vulvar cancers.
This may be due to the presence of three different types of epithelial tissue.
Inflammation of the Skene’s glands and Bartholin glands may appear similar to cystocele.
