 A medical procedure used in prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities and fetal infections.
A medical procedure used in prenatal diagnosis of chromosomal abnormalities and fetal infections.
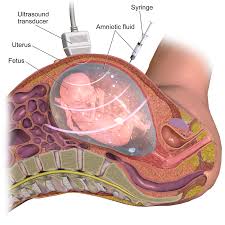
Amniotic fluid is sampled from the amnion or amniotic sac surrounding a developing fetus, and the fetal DNA is examined for genetic abnormalities.
Can determine the sex of the fetus with this technique.
A needle is inserted through the mother’s abdominal wall, the wall of the uterus, and into the amniotic sac with the aid of ultrasound-guidance.
Approximately 20 ml of amniotic fluid is extracted during the procedure.
After the amniotic fluid is extracted, the fetal cells are separated and grown in a culture medium, fixed and stained and their chromosomes are examined for abnormalities.
The most common abnormalities detected are Down syndrome trisomy 21, Edwards syndrome trisomy 18, and Turner syndrome monosomy X.
In pregnancies of longer than 30 weeks, the fetal lung maturity may be tested by sampling the amount of surfactant in the amniotic fluid by amniocentesis.
Amniotic fluid is replenished over the next 24–48 hours.
1% risk of ruptured membranes.
