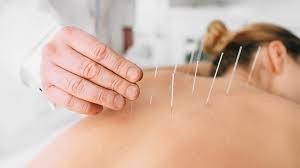
 Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in which thin needles are inserted into the body.
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine and a component of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in which thin needles are inserted into the body.
Acupuncture is a pseudoscience.
The theories and practices of TCM are not based on scientific knowledge.
Traditional Chinese medicine has been characterized as quackery.
It is most often used to attempt pain relief, and is generally used only in combination with other forms of treatment.
Trials and systematic reviews generally provide no good evidence of benefit, which suggests that it is not an effective method of healthcare.
Acupuncture is generally safe when done by appropriately trained practitioners using clean needle technique and single-use needles.
It has a low rate of mostly minor adverse effects.
The most frequently reported adverse events were pneumothorax and infections.
Acupuncture is a form of alternative medicine, used most commonly for pain relief.
It is also used to treat a wide range of conditions, and is generally only used in combination with other forms of treatment: heat, pressure, or laser light.
Acupuncture involves the insertion of thin needles into the skin.
Approximately five to twenty needles are inserted for ten to twenty minutes.
Classically, acupuncture is individualized and based on philosophy and intuition, and not on scientific research.
Traditional acupuncture involves needle insertion, moxibustion, and cupping therapy.
Traditional acupuncture believes that a life force circulates within the body in lines called meridians.
Western medical acupuncture approach involves using acupuncture after a medical diagnosis.
There is no defined standard for acupuncture points.
In traditional acupuncture, the acupuncturist decides which points to treat by observing and questioning the patient.
In TCM, the four diagnostic methods are: inspection, auscultation and olfaction, inquiring, and palpation.
Inspection focuses on the face and particularly on the tongue.
Tongue analysis includes size, shape, tension, color and coating, and the absence or presence of teeth marks around the edge.
Auscultation and olfaction involve listening for particular sounds such as wheezing.
Olfaction involves observing body odor.
Inquiring involves inquiries: chills and fever; perspiration; appetite, thirst and taste; defecation and urination; pain; sleep; and menses and leukorrhea.
Palpation focuses on feeling the body for tenderness points and feeling the pulse.
Stimulation of acupuncture points employs penetration of the skin by thin metal needles, which are manipulated manually.
The needle may be further stimulated by electrical stimulation.
Acupuncture needles are typically made of stainless steel.
Needles are usually disposed of after each use to prevent contamination.
Needles vary in length between 13 and 130 millimetres (0.51 and 5.12 in).
The shorter needles used near the face and eyes, while longer needles in areas with thicker tissues.
Needle diameters vary from 0.16 mm (0.006 in) to 0.46 mm (0.018 in), with thicker needles used on larger patients.
Needles may be manipulated: spinning, flicking, or moving up and down relative to the skin.
Often the needles are stimulated by hand in order to cause a dull, localized, aching sensation.
Acupuncture can be painful.
De-qi refers to a claimed sensation of numbness, distension, or electrical tingling at the needling site, indicating an accurate location of the acupoint.
Acupressure, uses physical pressure applied to acupressure points by the hand or elbow, or with various devices.
Acupuncture is often accompanied by moxibustion.
Moxibustion is the burning of cone-shaped preparations of moxa on or near the skin, often but not always near or on an acupuncture point.,
Acupuncture is used to treat acute conditions while moxibustion was used for chronic diseases.
Cupping therapy is a form of alternative medicine in which a local suction is created on the skin; practitioners believe this mobilizes blood flow in order to promote healing.
Tui na is a TCM method of attempting to stimulate the flow of qi by various bare-handed techniques that do not involve needles.
Electroacupuncture is a form of acupuncture in which acupuncture needles are attached to a device that generates continuous electric pulses, essentially transdermal electrical nerve stimulation.
Acupuncture point injection is the injection of various substances into acupoints.
Auriculotherapy, commonly known as ear acupuncture, auricular acupuncture, or auriculoacupuncture, involves inserting needles to stimulate points on the outer ear.
There is no scientific evidence that it can cure disease,and the evidence of its effectiveness is negligible.
Scalp acupuncture is based on reflexological considerations regarding the scalp.
Hand acupuncture, centers around reflex zones of the hand.
Medical acupuncture attempts to integrate reflexological concepts, the trigger points and dermatome distribution into acupuncture practice,
Cosmetic acupuncture is the use of acupuncture in an attempt to reduce facial wrinkles.
Bee venom acupuncture is a treatment approach of injecting purified, diluted bee venom into acupoints.
The efficacy of acupuncture for the treatment of various adult health conditions, but there was no robust evidence it was beneficial for anything, except shoulder pain and fibromyalgia.
Some suggest that most, if not all, benefits are due to the placebo effect, and strongly suggestive that acupuncture had no beneficial therapeutic effects at all.
Researchers usually find it does not matter where the needles are inserted, how often or even if needles are actually inserted, as sham or placebo acupuncture generally produces the same effects as ‘real’ acupuncture and, in some cases, does better.
A meta-analysis found little evidence that the effectiveness of acupuncture on pain, as compared to sham, was modified by the location of the needles, the number of needles used, the experience or technique of the practitioner, or by the circumstances of the sessions.
While some research suggests acupuncture can alleviate pain, the majority of research suggests that acupuncture’s effects are mainly due to placebo.
Any benefits of acupuncture are short-lasting.
There is insufficient evidence to support use of acupuncture compared to mainstream medical treatments, and it is not better than mainstream treatment in the long term.
Acupuncture is generally safe when administered by an experienced, appropriately trained practitioner using clean-needle technique and sterile single-use needles.
Contraindications to acupuncture include: coagulopathy, anticoagulant use, severe psychiatric disorders, and skin infections or skin trauma.
Electroacupuncture should be avoided at the spot of implanted electrical devices.
Serious adverse events were reported from developed countries: infections, organ trauma, with most frequent adverse events included pneumothorax, and bacterial and viral infections.
The majority of the reported adverse events were relatively minor, and the incidence is low.
Acupuncture seems to be safe in people getting anticoagulants.
The incidence of serious adverse events is 5 per one million, which included children and adults.
When used during pregnancy, the majority of adverse events caused by acupuncture were mild and transient, with most frequent mild adverse event was needling or unspecified pain, followed by bleeding.
The estimated incidence of adverse events following acupuncture in pregnant women was 131 per 10,000.
TCM theory and practice are not based upon the body of knowledge related to health, disease, and health care that has been widely accepted by the scientific community.
Many acupuncturists attribute pain relief therelease of endorphins when needles penetrate, but they do not support the idea that acupuncture can affect a disease.
