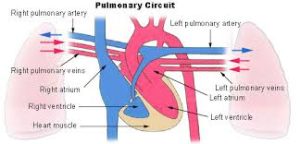
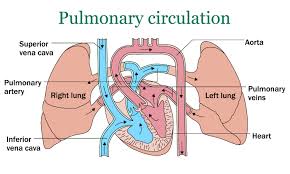
 The pulmonary circulation begins with deoxygenated blood returned from the body to the right atrium of the heart where it is pumped out from the right ventricle to the lungs.
The pulmonary circulation begins with deoxygenated blood returned from the body to the right atrium of the heart where it is pumped out from the right ventricle to the lungs.
In the lungs the blood is oxygenated and returned to the left atrium to complete the circuit.
The systemic circulation that begins with receiving the oxygenated blood from the pulmonary circulation into the left atrium.
From the atrium the oxygenated blood enters the left ventricle where it is pumped out to the rest of the body, returning as deoxygenated blood back to the pulmonary circulation.
The blood vessels of the pulmonary circulation are the pulmonary arteries and the pulmonary veins.
A separate circulatory circuit known as the bronchial circulation supplies oxygenated blood to the tissue of the larger airways of the lung.
De-oxygenated blood leaves the heart, goes to the lungs, and then enters back into the heart.
De-oxygenated blood leaves through the right ventricle through the pulmonary artery.
From the right atrium, the blood is pumped through the tricuspid valve into the right ventricle.
Blood is then pumped from the right ventricle through the pulmonary valve and into the pulmonary artery.
The pulmonary arteries carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs, where carbon dioxide is released and oxygen is picked up during respiration.
Arteries are further divided into very fine capillaries which are extremely thin-walled.
The pulmonary veins return oxygenated blood to the left atrium of the heart.
The pulmonary arteries have both an internal and external elastic membrane, whereas pulmonary veins have a single elastic layer.
Oxygenated blood leaves the lungs through pulmonary veins, it is returned it to the left part of the heart, completing the pulmonary cycle.
This blood then enters the left atrium, which pumps it through the mitral valve into the left ventricle.
From the left ventricle, the blood passes through the aortic valve to the aorta, andvis then distributed to the body through the systemic circulation before returning again to the pulmonary circulation.
From the right ventricle, blood is pumped through the pulmonary valve into the left and right main pulmonary artery, one for each lung.
The left and right main pulmonary arteryes branch into smaller pulmonary arteries that spread throughout the lungs.
The pulmonary circulation loop is virtually bypassed in fetal circulation.
The fetal lungs are collapsed, and blood passes from the right atrium directly into the left atrium through the foramen oval, an open conduit between the paired atria, or through the ductus arterioles, a shunt between the pulmonary artery and the aorta.
When the lungs expand at birth, the pulmonary pressure drops and blood is drawn from the right atrium into the right ventricle and through the pulmonary circuit.
Over the course of several months, the foramen ovale closes, leaving a shallow depression known as the fossa ovalis.
Pulmonary hypertension refers to an increase in resistance in the pulmonary arteries.
Pulmonary embolism is occlusion or partial occlusion of the pulmonary artery or its branches by an embolus.
It is usually from the embolization of a blood clot from deep vein thrombosis and causes difficulty breathing or chest pain, is usually diagnosed through a CT pulmonary angiography or V/Q scan, and is often treated with anticoagulants.
