 The cardiac veins are responsible for draining deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle.
The cardiac veins are responsible for draining deoxygenated blood from the heart muscle.
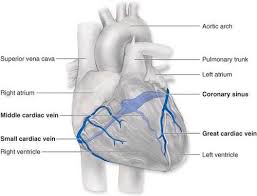
The Coronary Sinus is the largest cardiac vein.
It is located in the posterior coronary sulcus, receiveing blood from most cardiac veins.
The Coronary Sinus directly into the right atrium.
The Great Cardiac Vein begins at the heart apex, and runs in the anterior interventricular sulcus, continues in the coronary sulcus, and becomes the coronary sinus.
The middle cardiac vein runs in the posterior interventricular sulcus, drains the posterior portion of both ventricles and empties into the coronary sinus.
The Small Cardiac Vein is located in the right coronary sulcus, drains the right atrium and ventricle, and usually empties into the coronary sinus.
The Anterior Cardiac Veins are several small veins on the anterior surface of the heart and drain directly into the right atrium-Independent of the coronary sinus
These veins ensure proper venous drainage of the heart muscle, which is crucial for cardiac function.
The majority of cardiac veins ultimately drain into the coronary sinus, which then empties into the right atrium, allowing the deoxygenated blood to enter the pulmonary circulation for reoxygenation.
