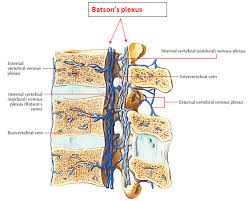
 The Batson venous plexus (Batson veins) is a network of valveless veins that connect the deep pelvic veins and thoracic veins draining the inferior end of the urinary bladder, breast and prostate to the internal vertebral venous plexuses.
The Batson venous plexus (Batson veins) is a network of valveless veins that connect the deep pelvic veins and thoracic veins draining the inferior end of the urinary bladder, breast and prostate to the internal vertebral venous plexuses.
Batson’s plexus refers to the vertebral venous plexus, a network of valveless veins located within the spinal column.
The vertebral venous plexus is significant for its role in the bidirectional flow of blood, which can facilitate the spread of tumors, infections, and emboli It also plays a role in the regulation of intracranial pressure and venous outflow from the brain.
Because of their location and lack of valves, they are believed to provide a route for the spread of cancer metastases.
These metastases commonly arise from cancer of the pelvic organs such as the rectum and prostate and may spread to the vertebral column or brain.
Batson’s plexus is part of the Cerebrospinal venous system.
Batson’s venous plexus may also allow the spread of infection in a similar manner: neuroschistomiasis Urinary tract infections like pyelonephritis have been shown to spread to cause osteomyelitis of the vertebrae via this route.
The osteomyelitis in such a case will resolve concurrently with the same antibiotic that treats the urinary tract infection because both infections are from the same organism.
