 Wartenberg’s syndrome (WS)is an entrapment neuropathy of the superficial radial nerve (SRN), a pure sensory nerve.
Wartenberg’s syndrome (WS)is an entrapment neuropathy of the superficial radial nerve (SRN), a pure sensory nerve.
WS is also known as “cheiralgia paraesthetica”.
It is related to the compression of the superficial radial nerve by the relative motion of brachioradialis and extensor carpi radialis longus during forearm rotation.
The nerve may be entrapped at its exit point by the intervening fascia.
The radial nerve bifurcates in the proximal forearm to give rise to SRN and posterior interosseous nerve.
The superficial radial nerve travels deep to the brachioradialis and lies on the undersurface of the muscl, and emerges between brachioradialis and extensor carpi radialis longus in the distal third forearm, to become superficial.
Symptoms of Wartenberg’s syndrome
Vague pain over the dorsoradial hand Paraesthesia Numbness
Onset may have been precipitated by: tight bracelet, wrist watch, wrist band minor trauma to the wrist repetitive wrist flexion, ulnar deviation or forearm rotation
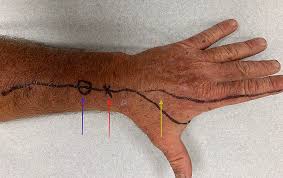
A positive Tinel’s sign over the superficial radial nerve at the entrapment spot is the most reliable sign.
A provocative test with repeated wrist flexion, ulnar deviation and pronation can suggest the diagnosis.
Nerve conduction studies can be normal.
Diagnostic local anaesthetic injection is the most useful test:
Injection of 1-2ml of fast-acting local anaesthetic (1 or 2% lidocaine) at the Tinel’s spot followed by resolution of the above symptoms is regarded as a positive test for nerve entrapment. Should the symptoms return predictably as the local anaesthetic wears off (after 4 hours), that is taken as a further level of confirmation. Treatment
Nonoperative
Removal of tight wrist wear Activity modification Splint Painkillers Operative
Surgical decompression (neurolysis) of the SRN
